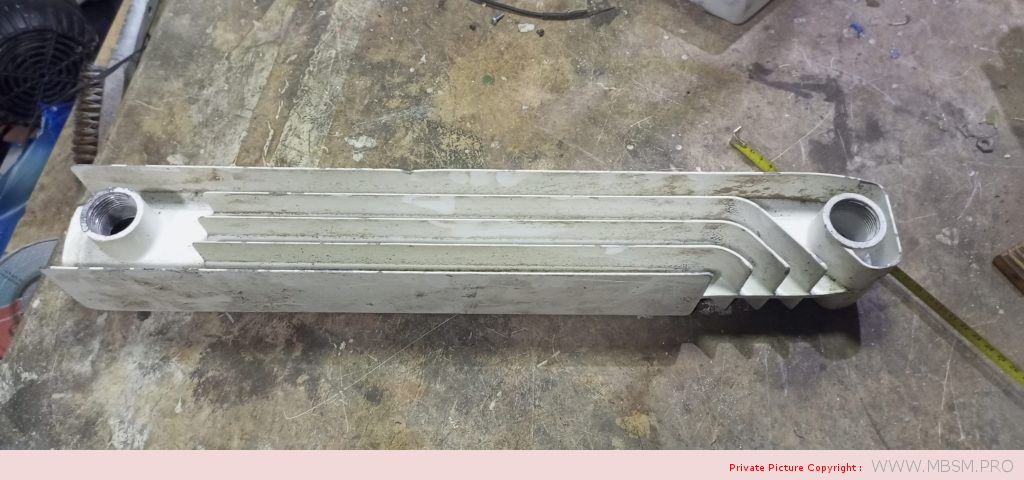
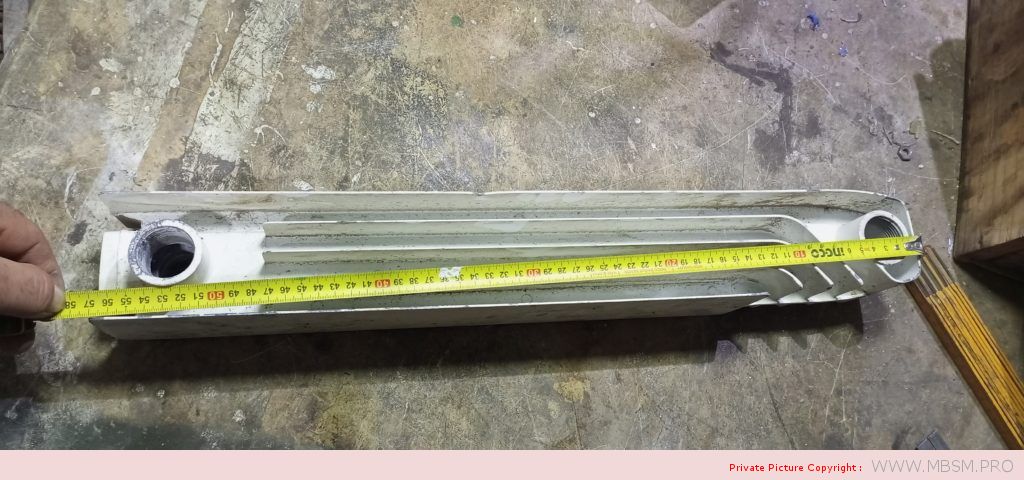
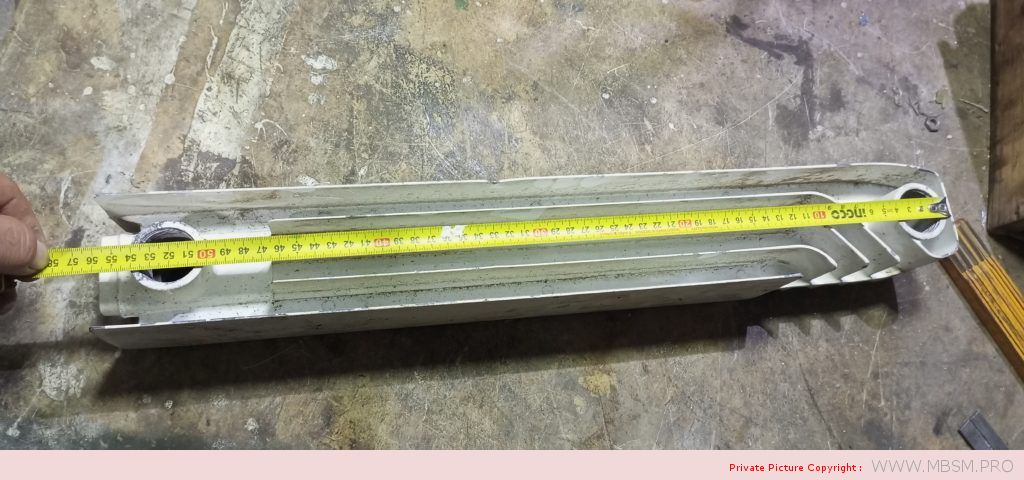
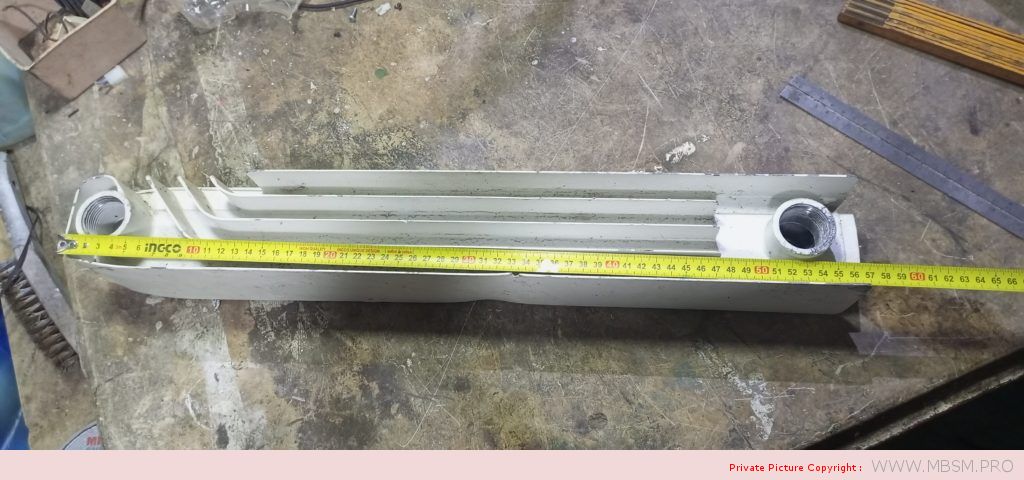
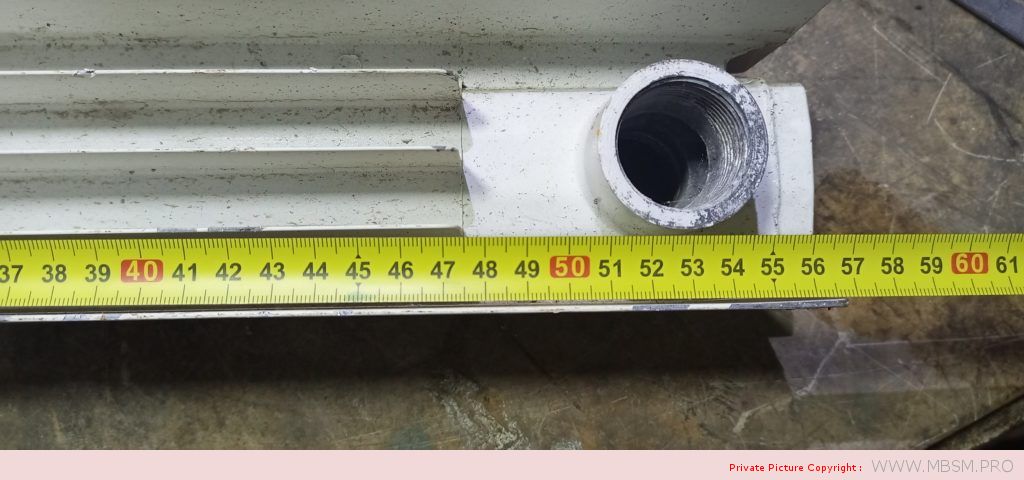
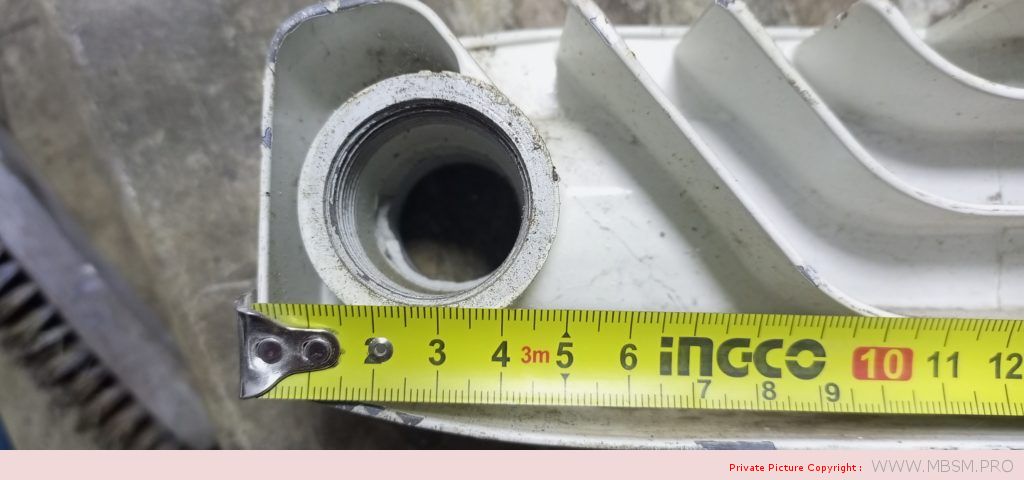
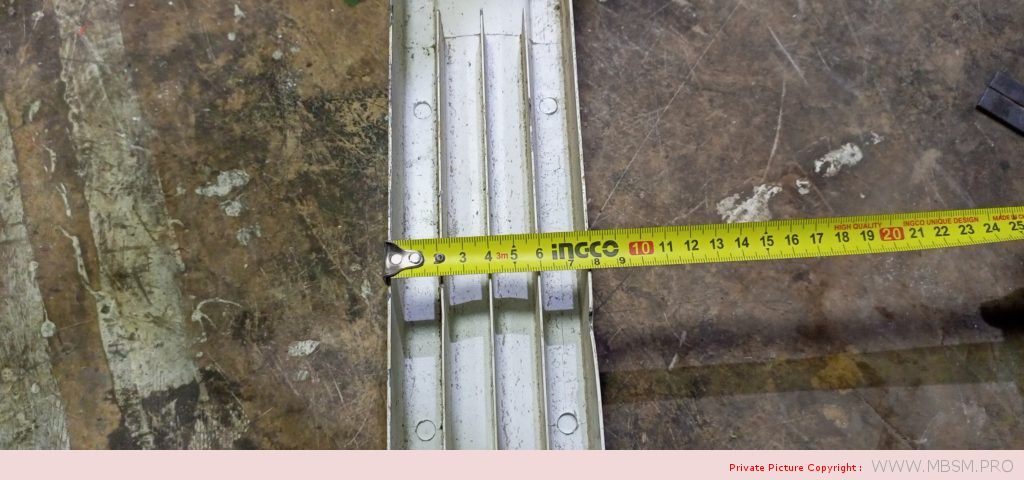

















Radiator
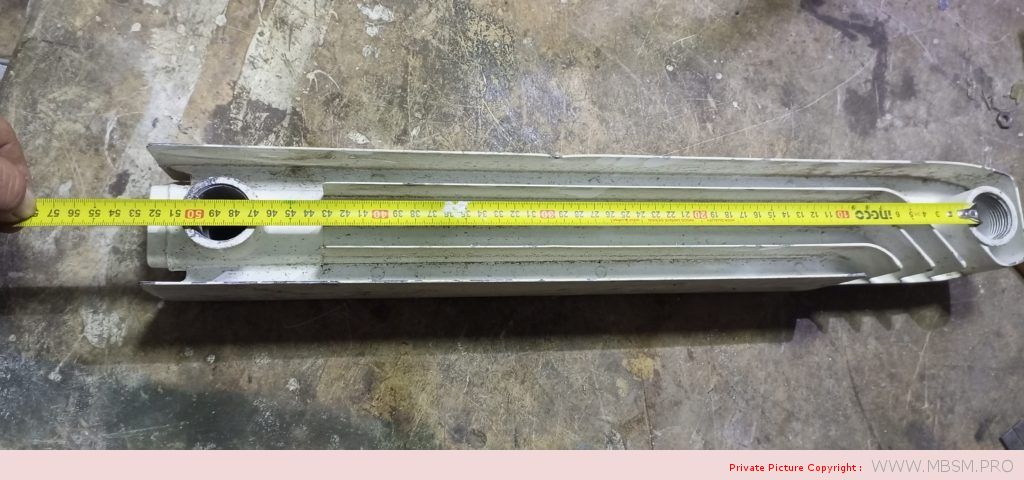
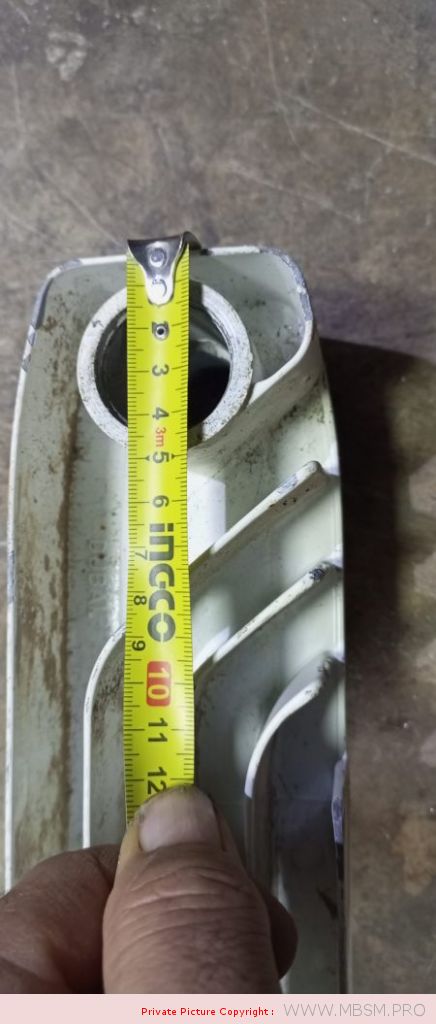
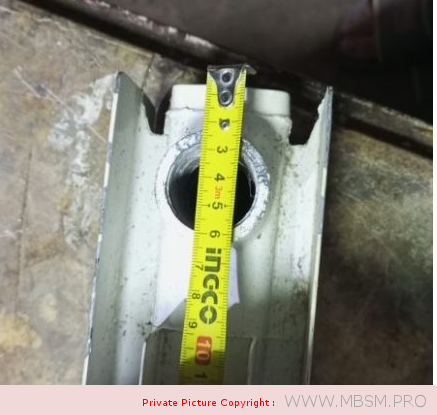
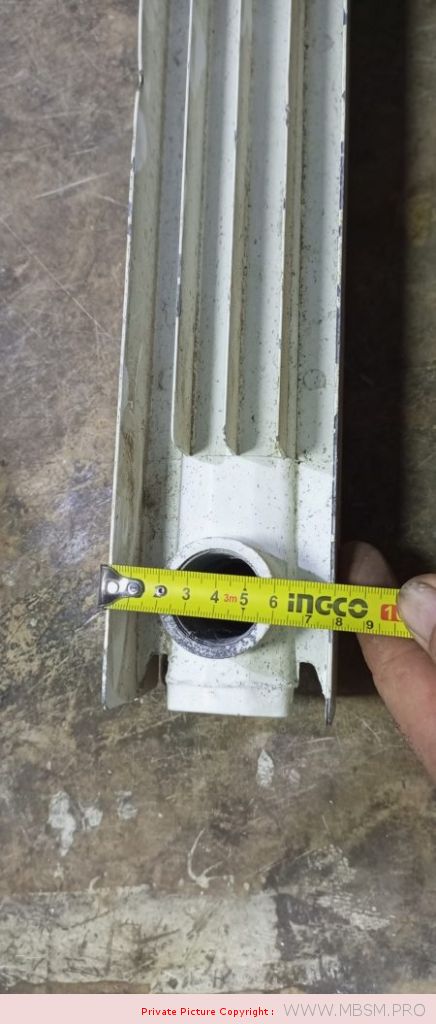
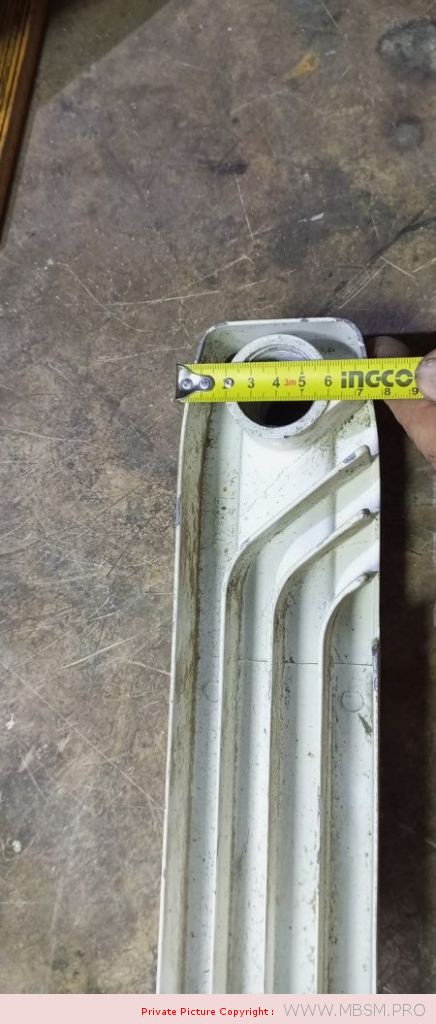
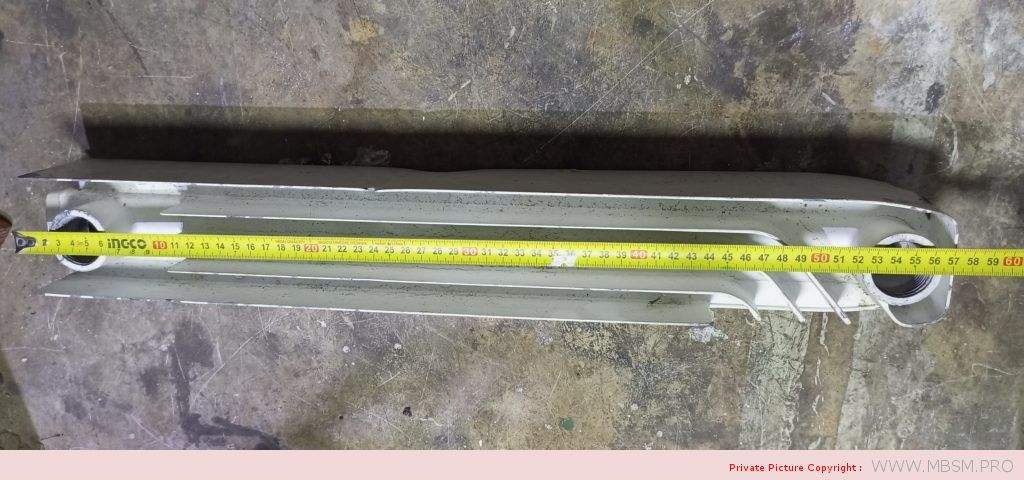
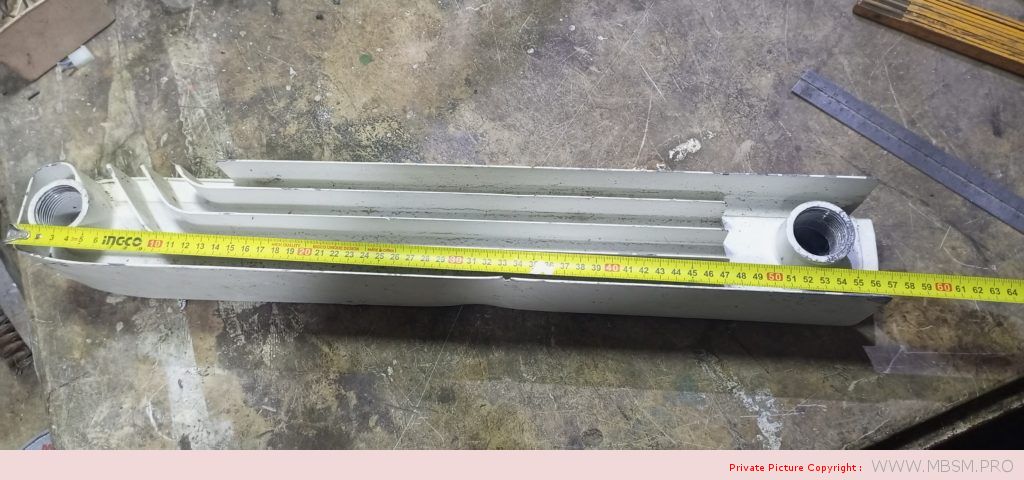
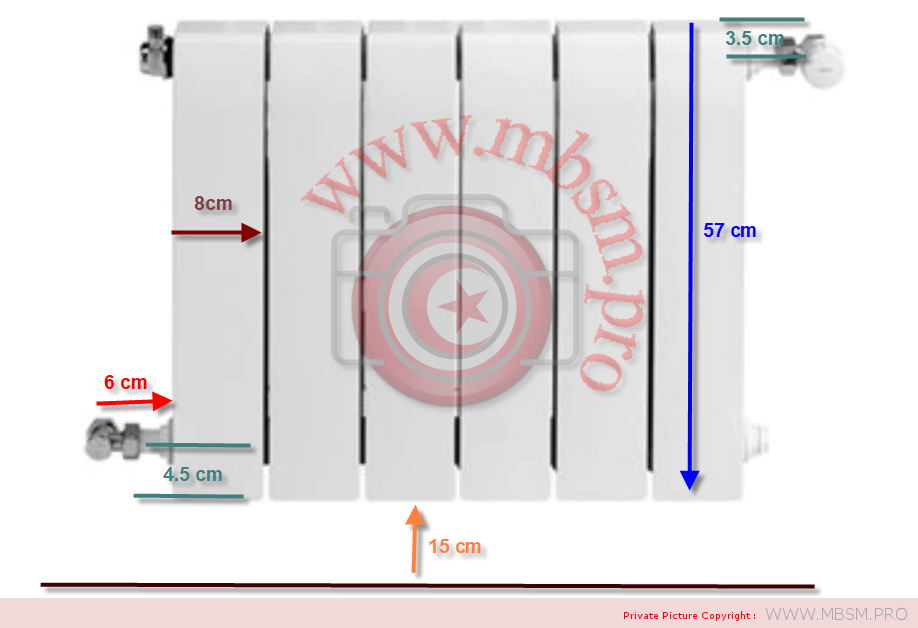
َAuminum radiators 57 cm high, 8 cm wide and 7 cm thick, with a calorific power 104 W

Calculation of heating capacity in terms of room volume
First, we calculate the volume of the room by multiplying the length by the width by
Height :
Example: A room whose dimensions are (3.6 m) length (3.25 m) width (2.6 m) height means its size is 3.6 x 3.25 x 2.6 = 30.42 m 3 In most cases, buildings in Algeria have external walls that do not have an insulating material for cold and heat, so we must multiply the volume The room in (2) and if it is isolated, we multiply by (1).
As it is known, the temperature and cold changes from one region to another. For example, the average cold in the high plateaus reaches minus 5 sometimes at night, while in the north of the country, the average cold may reach 5 degrees in the worst case, and the appropriate temperature in the house is from 20 to 22 degrees, meaning that the difference in degrees In the capital, the temperature is 22 minus 3, which is equal to 19 degrees, and in the higher plateaus the difference is 22 minus -5, which is equal to 27 degrees. We multiply the room volume by the insulation coefficient, if it is 1 and if not 2, then we multiply the volume of the room by 2 by the temperature difference in our previous example. The room is 30.42 The insulation coefficient is 2 The temperature difference is 19. When we multiply the volume by the coefficient by the temperature difference, we get 30.42 x 2 x 19 = 115.96 for the northern regions and 30.42 x 2 x 27 = 1642.68 for the high plateaus.
Since the calorific value of each radiator element varies according to type, material and size, in all our calculations for an aluminum radiator, the approximate heat value is 150. If we divide what we get by 150, we get the number of units, i.e. 1155.96 ÷ 150 = 7.7 meaning that the required radiator is 8 elements For a room in the north of the country, and for a room in the high hills, 1642.68 ÷ 150 = 10.95, meaning that the required radiator is 11 or 12 elements.
حساب قدرة التدفئة من حيث حجم الغرفة
أولا نحسب حجم الغرفة وهذا بضرب الطول في العرض في
الإرتفاع :
مثال : غرفة أبعادها هم (3.6م) طول (3.25م)عرض( 2.6م )إرتفاع يعني حجمها هو 3.6×3.25×2.6=30.42م³ في غالب الأحيان البنايات في الجزائر جدرانها الخارجية ليست لديها مادة عازلة للبرد والحرارة لذا وجب ان نضرب حجم الغرفة في (2) وإن كانت معزولة نضرب في (1).
كما هو معروف تتغير درجة الحراره والبرودة من منطقة لأخرى فمثلا يصل معدل البرودة في الهضاب العليا إلى ناقص 5 أحيانا بالليل بينما في شمال الوطن فمعدل البرودة قد يصل إلى 5 درجات في أسوأ الأحوال والحرارة المناسبة في المنزل هي من 20 إلى22 درجة أي أن الفارق في درجة الحرارة في العاصمة هو 22 ناقص 3 ويساوي 19 درجة وفي الهضاب العليا الفرق هو 22 ناقص -5 ويساوي 27درجة نضرب حجم الغرفة في معامل العزل إن كان موجود 1 وإن لم يكن 2 إذن نضرب حجم الغرفة في 2 في فرق درجة الحرارة في مثالنا السابق لدينا حجم الغرفة هو 30.42 معامل العزل هو 2 فرق درجة الحرارة هو 19 لما نضرب الحجم في المعامل في فرق الحرارة نحصل 30.42×2×19=1155.96 بالنسبة للمناطق الشمالية و30.42×2×27=1642.68 بالنسبة للهضاب العليا .
بما أن القيمة الحرارية لكل عنصر من الرادياتور تختلف حسب النوع والمادة والحجم الى أنه في جميع حساباتنا بالنسبة لرادياتور ألمنيوم القيمة الحراره التقريبية هي 150 إذا نقسم ما تحصلنا عليه على 150 فنحصل على عدد الوحدات أي 1155.96÷150=7.7 بمعنى أن الرادياتور المطلوب هو 8 عناصر بالنسبة لغرفة في شمال الوطن و أما بالنسبه لغرفة في الهضاب العليا 1642.68÷150=10.95 أي أن الرادياتور المطلوب هو 11 عنصر أو 12 عنصر.
Calcul de la capacité de chauffage en fonction du volume de la pièce
Tout d’abord, nous calculons le volume de la pièce en multipliant la longueur par la largeur par
Hauteur :
Exemple : Une pièce dont les dimensions sont (3,6 m) longueur (3,25 m) largeur (2,6 m) hauteur signifie que sa taille est de 3,6 x 3,25 x 2,6 = 30,42 m 3 Dans la plupart des cas, les bâtiments en Algérie ont des murs extérieurs qui n’ont pas de matériau isolant pour le froid et le chaud, il faut donc multiplier le volume La pièce en (2) et si elle est isolée, on multiplie par (1).
Comme on le sait, la température et le froid varient d’une région à l’autre. Par exemple, le froid moyen dans les hauts plateaux atteint parfois moins 5 la nuit, tandis que dans le nord du pays, le froid moyen peut atteindre 5 degrés dans les pire des cas, et la température appropriée dans la maison est de 20 à 22 degrés, ce qui signifie que la différence en degrés Dans la capitale, la température est de 22 moins 3, ce qui est égal à 19 degrés, et dans les plateaux supérieurs la différence est de 22 moins -5, ce qui est égal à 27 degrés. On multiplie le volume de la pièce par le coefficient d’isolation, s’il est de 1 et sinon 2, alors on multiplie le volume de la pièce par 2 par la différence de température dans notre exemple précédent. pièce est de 30,42 Le coefficient d’isolation est de 2 La différence de température est de 19. Quand on multiplie le volume par le coefficient par la différence de température, on obtient 30,42 x 2 x 19 = 115,96 pour les régions du nord et 30,42 x 2 x 27 = 1642,68 pour la hauts plateaux.
Étant donné que la valeur calorifique de chaque élément de radiateur varie selon le type, le matériau et la taille, dans tous nos calculs pour un radiateur en aluminium, la valeur calorifique approximative est de 150. Si nous divisons ce que nous obtenons par 150, nous obtenons le nombre d’unités, c’est-à-dire 1155,96 150 = 7,7 signifiant que le radiateur requis est de 8 éléments Pour une pièce au nord du pays, et pour une pièce dans les hautes collines, 1642,68 ÷ 150 = 10,95, c’est-à-dire que le radiateur requis est de 11 ou 12 éléments.

| Attachment | Type | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-12 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture270793653_433135355196792_4947958198959085989_n | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_PDF_Auminum-radiators-Baxi-57-cm-high-8-cm-wide-and-7-cm-thick-with-a-calorific-power-104-W-Element-dimension-and-measure | application/pdf | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_radiateur | image/png | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_radiateur-1 | image/png | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_radiateur-2 | image/png | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-17 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-16 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-15 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-14 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-13 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-1 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-11 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-10 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-9 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-8 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-7 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-6 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-5 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-4 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-3 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
| Mbsm_dot_pro_private_picture_Radiateur-en-aluminium-2 | image/jpeg | Get Link |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |
 | Image | View Image |



