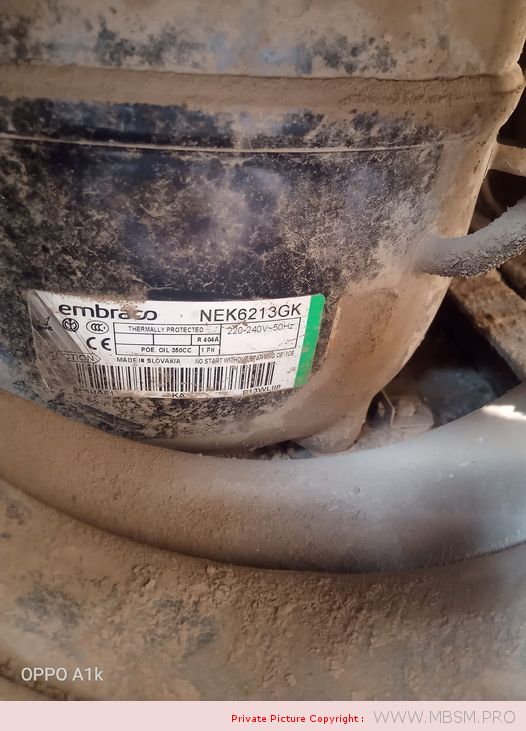
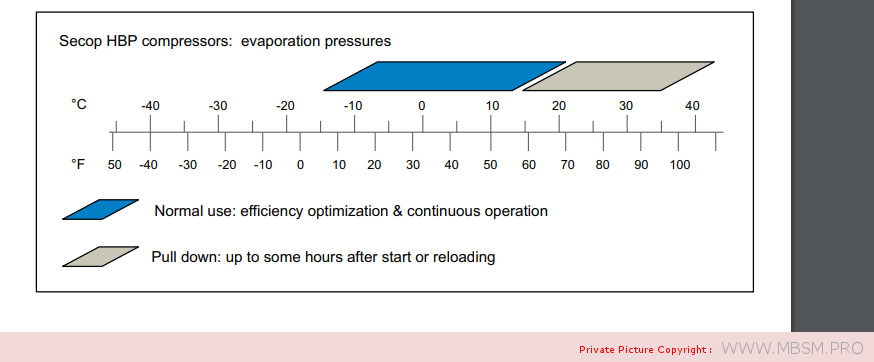
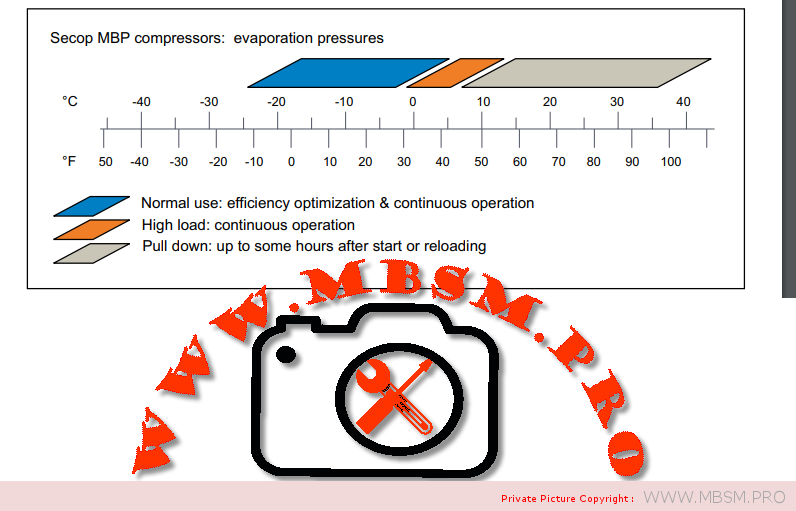
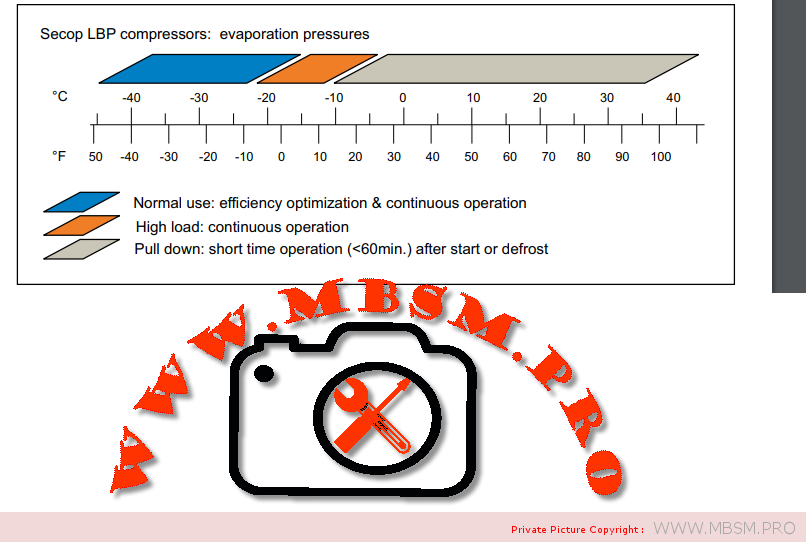
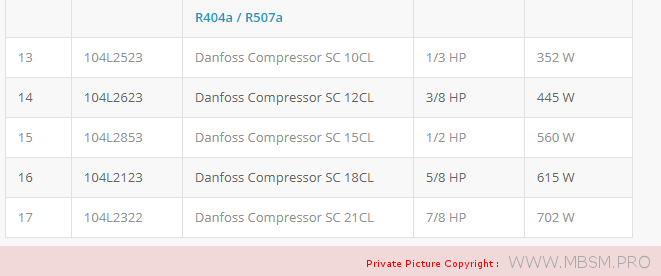
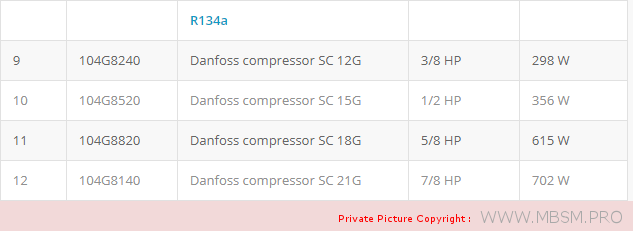
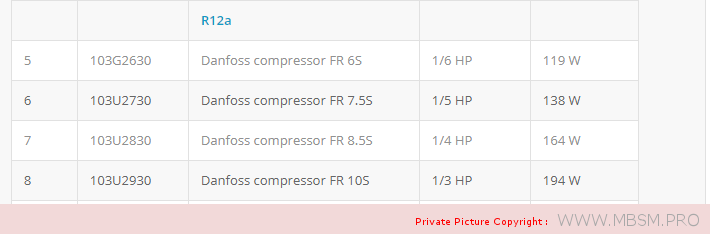
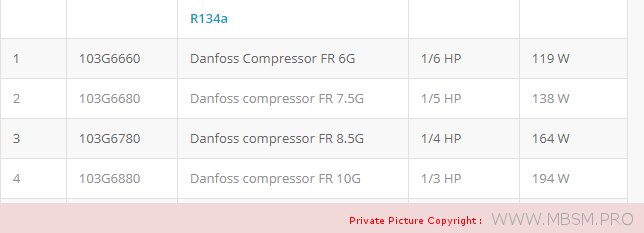
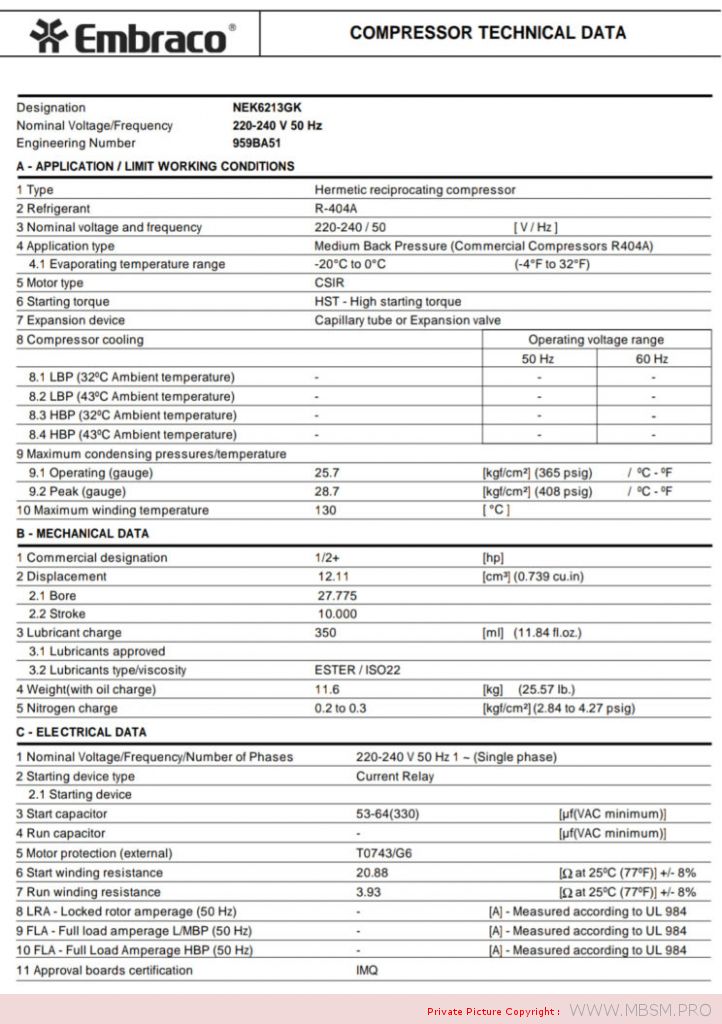
Types of Electrical Motors, RSIR, CSIR, RSCR, CSR, PTC, NTC, LST, HST, MBP, HBP, LBP
Types of Electrical Motors
RSIR (Resistance Start-Induction Run)
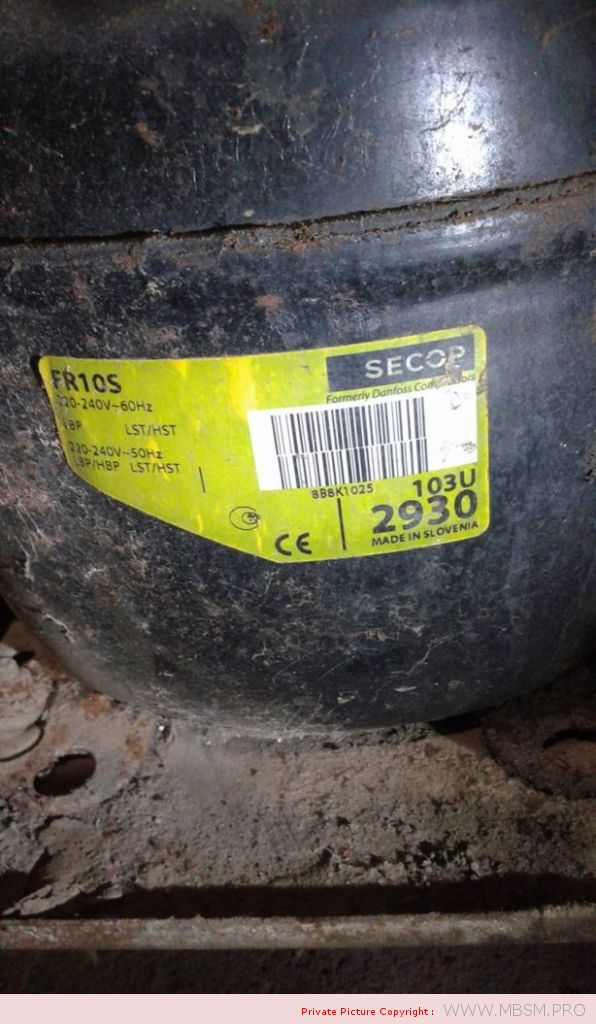
LST motor. No capacitors. Auxiliary winding is disconnected after start
up. Standard energy efficiency.
CSIR (Capacitor Start-Induction Run)
HST motor. With starting capacitor.
Auxiliary winding is disconnected after start up. Standard efficiency.
RSCR (Resistance Start-Capacitor Run)
LST motor. With running capacitor. Auxiliary winding remains
connected after start up.
Used for high efficiency in small capacity compressors (particularly in
household refrigeration)
CSR (Capacitor Start and Run)
HST motor. Two capacitors (starting and running).
Auxiliary winding remains connected after start up.
Used for high efficiency in small compressors and for size reduced
size motors in compressors with comparatively large displacements
Type of starting device
Current relay – (electromechanical). RSIR/CSIR motors and CSR low/
medium-power motors with NTC (the NTC is connected in series with
the starting capacitor and the main purpose is to reduce the current
peaks in the relay contacts)
Potential relay – (electromechanical). CSR high-power motors.
PTC – (Positive Temperature Coefficient), the resistance increases
with the temperature. Device only with RSIR or RSCR motors in the
(Small L, B), L and P ranges.
NTC – (Negative Temperature Coefficient), the resistance decreases
with the temperature. Used in some CSR in order to reduce
dimensions and components.

Type of torque
LST – Low Starting Torque – Systems with capillary tube or balanced
pressures at start up.
HST – High Starting Torque – Systems with expansion valve or
capillary tube, with unbalanced pressures at start up.